The quality of covered yarn is not determined by a single element, but by a complex interplay of material selection, manufacturing precision, and environmental control. From the inherent properties of raw materials to the final inspection, each step in the production process presents critical control points that directly impact the yarn’s performance, consistency, and suitability for its end-use.
This guide provides a detailed examination of the multifaceted factors that define covered yarn quality, offering manufacturers a framework for achieving excellence and consistency in their products.

Raw Materials
Covered yarn production hinges on two critical components: the Core Yarn and the Covering Yarn. The core, typically Spandex or rubber, is the “engine” determining elasticity, recovery, and durability, often judged by its 500-700% elongation capability. The covering yarn, made of materials like Nylon or Cotton, forms the protective “sheath,” dictating surface characteristics, hand feel, and processing viability. This article dives into the technical specifications—from denier consistency and tenacity to yarn evenness—explaining why rigorous material selection and quality control of both the core and the cover are the absolute first steps in ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the final textile product.
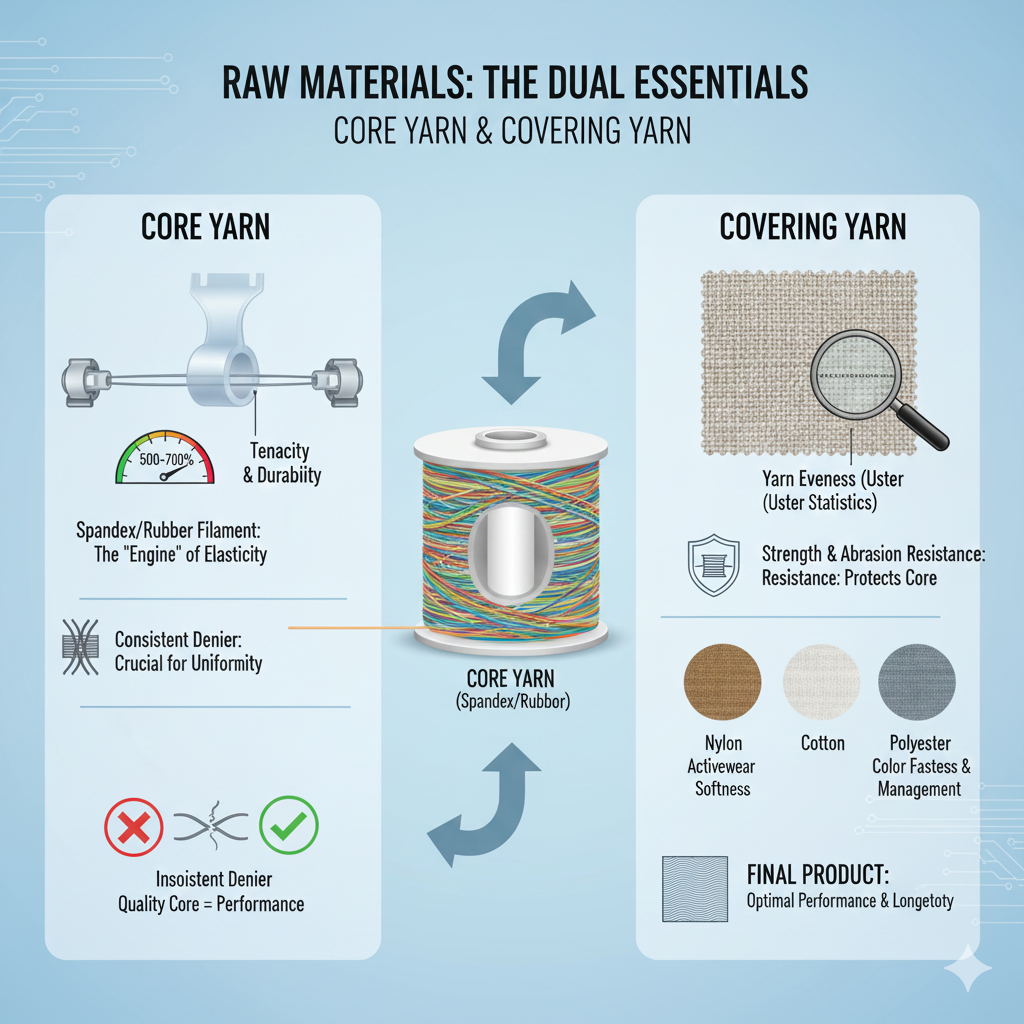
Core Yarn
The core yarn serves as the fundamental engine of elasticity in covered yarns, dictating the stretch performance and recovery characteristics of the final product. Its properties directly determine how the yarn will behave under tension and throughout its lifecycle, making core selection a critical first step in quality assurance.
The elasticity and recovery properties define the yarn’s functional performance, with high-grade spandex typically offering 500-700% elongation with near-perfect recovery, while rubber cores provide different elastic characteristics. This is measured through elongation and recovery tests during quality control.
The tenacity and durability of the core yarn must withstand both the mechanical stresses of the covering process and the demands of end-use applications, with core yarn denier consistency being crucial for uniform elasticity. Inconsistent denier or poor tenacity leads to breakage during processing and premature failure in the final product.
Covering Yarn
The covering yarn creates the protective sheath and defines the surface characteristics of the final product, influencing everything from hand feel to durability and aesthetic appeal. This outer layer determines how the yarn interacts with both manufacturing processes and end-users, making material selection equally critical as core choice.
Fiber content selection directly impacts the final product’s properties, with nylon providing excellent durability for activewear, cotton offering natural softness for comfort wear, and polyester delivering superior color fastness and moisture management.
The yarn evenness, measured through Uster statistics, ensures consistent coverage and prevents “grin-through” where the core becomes visible when stretched. Strength and abrasion resistance qualities protect the delicate core during subsequent weaving/knitting processes, while proper twist level and stability prevent excessive torque that can cause spirality in knitted fabrics. Quality control measures for covering yarn include yarn count verification, tensile strength testing, and evenness analysis to ensure consistent performance throughout production.
Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing methodology employed in covered yarn production fundamentally shapes the final product’s characteristics, performance attributes, and suitable applications. Each technique imparts distinct structural properties that determine how the yarn will behave in subsequent textile manufacturing processes and end-use scenarios.
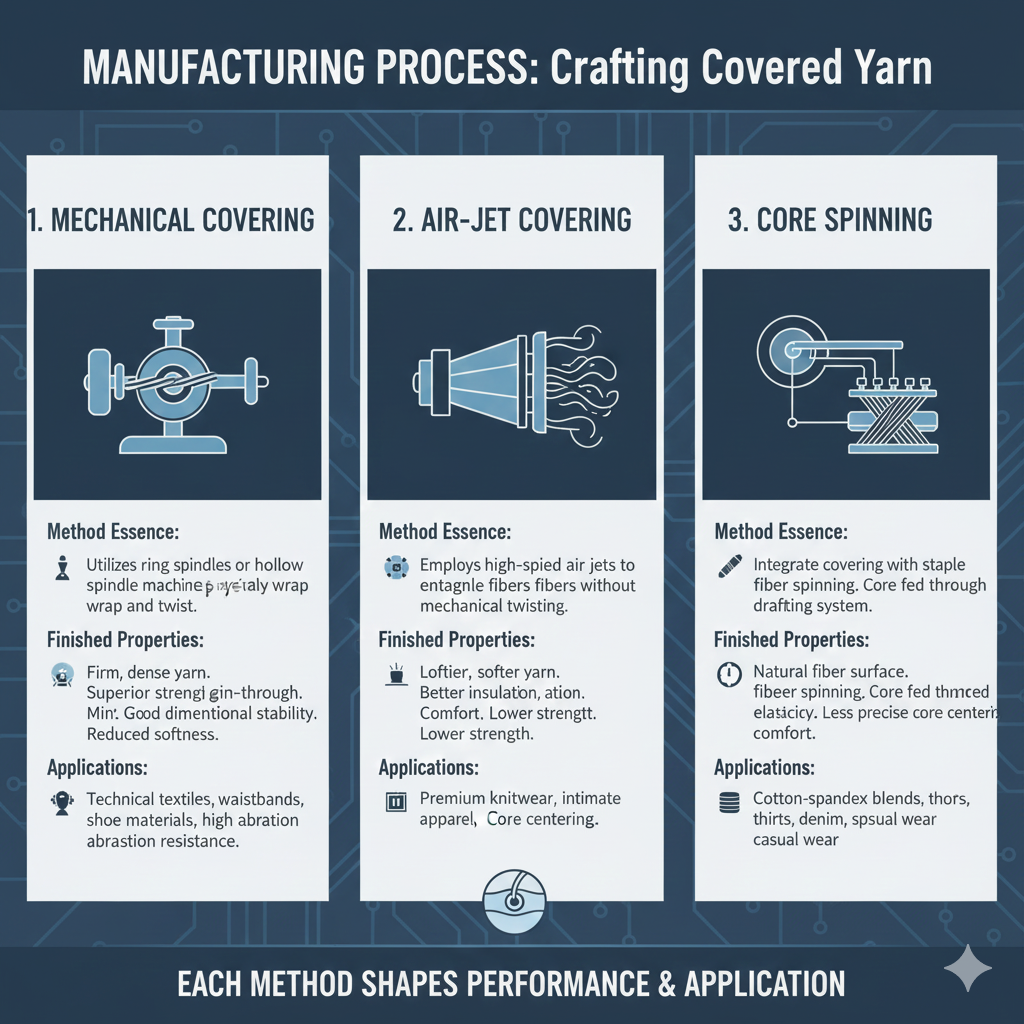
Mechanical Covering
- Method Essence: Utilizes ring spindles or hollow spindle machines to physically wrap and twist the covering yarn around the elastane core in a precise, controlled manner.
- Finished Properties: Produces firm, dense yarn with superior strength, minimal grin-through, and good dimensional stability, though with somewhat reduced softness.
- Applications: Ideal for technical textiles, waistbands, shoe materials, and applications requiring high abrasion resistance and structural integrity.
Air-Jet Covering
- Method Essence: Employs high-speed air jets to entangle the covering fibers around the core through turbulent air flow without mechanical twisting.
- Finished Properties: Results in loftier, softer yarn with better insulation properties and comfort, though with potentially lower strength compared to mechanical covering.
- Applications: Perfect for premium knitwear, intimate apparel, sportswear, and any application prioritizing comfort and softness over extreme durability.
Core Spinning
- Method Essence: Integrates the covering process with staple fiber spinning, where the elastane core is fed through the drafting system of a ring spinning frame and wrapped by staple fibers during twisting.
- Finished Properties: Produces yarn with natural fiber characteristics on the surface, good comfort, and balanced elasticity, though with potentially less precise core centering.
- Applications: Excellent for cotton-spandex blends in t-shirts, denim, casual wear, and products requiring the comfort of natural fibers with added stretch.
Environmental Conditions
Environmental factors throughout production and storage significantly impact covered yarn quality and performance consistency. Proper environmental control ensures material stability and processing reliability.
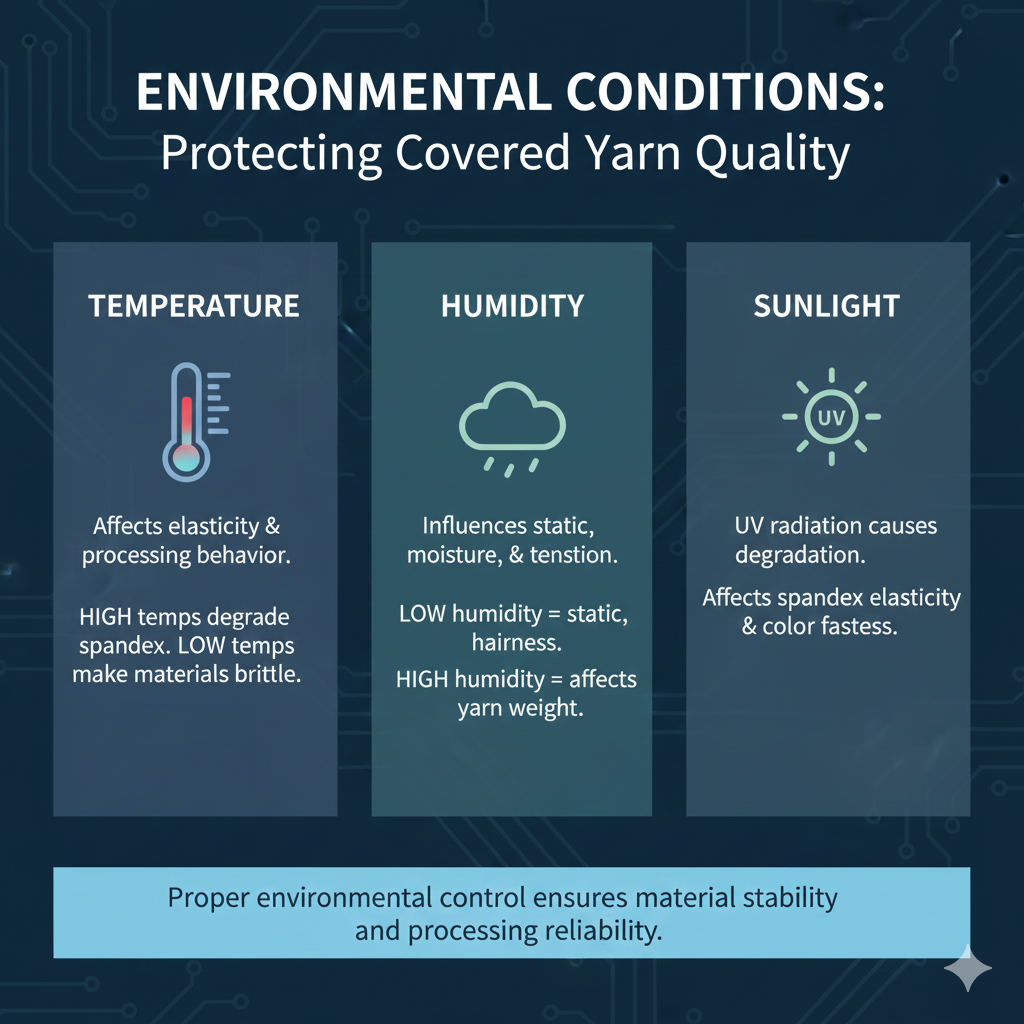
- Temperature: Affects material elasticity and processing behavior. High temperatures can degrade spandex elasticity, while low temperatures may make materials brittle.
- Humidity: Influences static electricity, fiber moisture content, and processing tension. Low humidity increases static, causing hairiness and processing issues, while high humidity affects yarn weight and dimensional stability.
- Sunlight: Prolonged exposure to UV radiation can cause degradation of both core and covering materials, particularly affecting spandex elasticity and color fastness.
Quality Control Indicators for Covered Yarn
Implementing a comprehensive quality control system across all production stages is essential for ensuring consistent covered yarn quality. This multi-phase approach identifies potential issues at the earliest possible stage, preventing costly downstream defects and ensuring final product reliability.

Before Production — Raw Material Testing
Thorough raw material testing establishes the foundation for quality by verifying that all incoming materials meet specified requirements before processing begins. The core yarn must demonstrate consistent denier measurements and reliable elasticity to ensure uniform performance, while covering yarn requires precise count verification and composition analysis to guarantee proper coverage and end-use suitability. Establishing strict raw material specifications prevents processing issues and ensures consistent end-product performance.
| Quality Indicator | What It Measures | Why It Matters | Standard / Expected Range | Testing Method |
| Core Yarn Denier Accuracy | Thickness of spandex or rubber core | Ensures stable stretch and final yarn uniformity | Must match spec; Low CV% | Denier Tester; Gravimetric Test |
| Covering Yarn Linear Density (Denier/Tex) | Mass per length of nylon/polyester covering yarn | Affects coverage density and fabric appearance | Precise per specification | Denier/Tex Tester |
| Yarn Evenness (U%, CV%) — Core & Covering Yarn | Variation in thickness | Influences uniform coverage and reduces defects | U% ≤ 12% | Uster Evenness Tester |
| Hairiness Level (Covering Yarn) | Short fibers protruding from surface | Impacts final appearance, snagging risk | Minimum hairiness for high-grade products | Uster Hairiness Tester |
| Tensile Strength (Core & Covering) | Breaking strength | Ensures durability and prevents breakage during production | As per material standards | Tensile Strength Tester |
| Elasticity & Recovery Rate (Spandex Core) | Stretch % and recovery ability | Essential for performance fabrics and seamless products | Recovery ≥ 90% | Tensile / Elongation Tester |
| Color Fastness (Dyed Covering Yarn) | Resistance to wash/light/rubbing | Ensures color stability during knitting and finishing | ISO 4–5 rating | ISO 105 Testing |
During Production — In-Process Monitoring
Continuous monitoring during manufacturing catches deviations in real-time, allowing for immediate corrections and maintaining process stability.
Maintaining optimal draft ratio and TPM (Twists Per Meter) ensures proper core activation and sheath integration, while consistent tension control and evenness monitoring prevent defects that could compromise final product quality. Real-time process control through systematic monitoring and adjustment ensures consistent quality throughout production runs.
| Quality Indicator | What It Measures | Why It Matters | Standard / Expected Range | Testing Method |
| Core Tension Consistency | Stability of tension applied to the core yarn | Prevents spirality, overstretching, and uneven recovery | ±1–3% deviation | Real-time Tension Meter |
| Covering Tension | Uniformity of the covering yarn tension | Avoids loose wrapping or excessive tightness | Must follow machine spec | In-line Tension Trajectory Sensor |
| Twist Level / TPM (Turns Per Meter) | Number of twists in SCY/DCY | Determines coverage density and yarn stability | SCY: 600–1200 TPM; DCY: 800–2000 TPM | Twist Tester |
| Interlacing Node Count (For ACY) | Number of air-jet nodes | Ensures yarn cohesion and prevents slippage/pilling | 30–60 nodes/m depending on grade | Interlace Node Tester |
| Coverage Uniformity | Even distribution of covering yarn on the core | Affects appearance and performance | No visible core exposure | Optical Inspection |
| Machine Speed Stability | Consistency of spindle/air-jet operation | High variation causes uneven yarn & breakage | Stable ± allowable RPM | Machine Monitoring System |
| Breakage Rate Monitoring | Frequency of yarn breaks | Indicates tension or material problems | As low as possible | Real-time Production Logs |
Table 2 — In-Process Quality Indicators
After Production — Final Product Testing
Comprehensive final testing validates that the finished yarn meets all specified requirements and performs as expected in end-use applications.
Final validation must confirm that elongation and recovery meet target specifications, grin-through remains within acceptable limits, and torque levels ensure trouble-free processing in subsequent manufacturing stages. Final product validation through rigorous testing ensures customer specifications are met and prevents quality issues in downstream manufacturing.
| Quality Indicator | What It Measures | Why It Matters | Standard / Expected Range | Testing Method |
| Final Linear Density Accuracy | Final denier of covered yarn | Ensures consistency with buyer specifications | Must match spec with low CV% | Denier Tester |
| Elasticity & Recovery (Finished Yarn) | Stretch & rebound of the final product | Critical for hosiery, sportswear, elastic bands | Elongation per product type; Recovery ≥ 90% | Tensile / Stretch Tester |
| Abrasion Resistance | Ability to resist surface wear | Important for socks, waistbands, leggings | High rub cycles | Martindale Abrasion Tester |
| Spirality/Uneven Wrapping Check | Presence of spirality or inconsistent wrapping | Impacts appearance and knitting behavior | No visible helical defects | Visual + Microscopic Inspection |
| Core Exposure Check | Exposure of spandex/rubber core | Indicates insufficient covering | 0% visible exposure | Optical Scan |
| Thermal Setting Stability | Behavior after heat exposure | Ensures dimensional stability in dyeing/knitting | Stable under required temperature | Heat-setting Oven Test |
| Package Density & Winding Quality | Consistency of bobbin winding | Prevents tension issues during knitting | No soft spots / hard spots | Package Density Tester |
| Final Appearance Grade | Overall visual quality: smoothness, color uniformity | Represents final product quality | Grade A | Visual Inspection |
Table 3 — Final Quality Indicators
Conclusion
The quality of covered yarn emerges from a sophisticated interplay between material science, manufacturing precision, and rigorous quality management. From the initial selection of core and covering materials through the choice of production methodology and environmental controls, each decision cascades through to the final product’s performance. Manufacturers who master these interconnected factors—implementing robust raw material testing, precise process control, and comprehensive final validation—position themselves to deliver consistent, high-performance covered yarns that meet the exacting demands of modern textile applications. In today’s competitive landscape, this systematic approach to quality is not merely advantageous but essential for sustainable business success.
Ready to elevate your covered yarn quality? Contact our technical specialists today to develop a comprehensive quality strategy tailored to your specific production needs and market requirements.
TANI THREAD CO., LTD
- Address: Thanh Hoa Hamlet, Thanh Dien Commune, Chau Thanh District, Tay Ninh Province, Vietnam
- Hotline: 0984.841.239
- Email: sale@tanithread.com
- Website: tanithread.com



