The selection of covering material is a critical determinant in the performance and application of elastic covered yarns. While the spandex core provides stretch, the covering yarn defines the fabric’s surface characteristics, durability, and comfort. This guide explores the most common covering materials and their key properties to inform optimal selection for textile production.
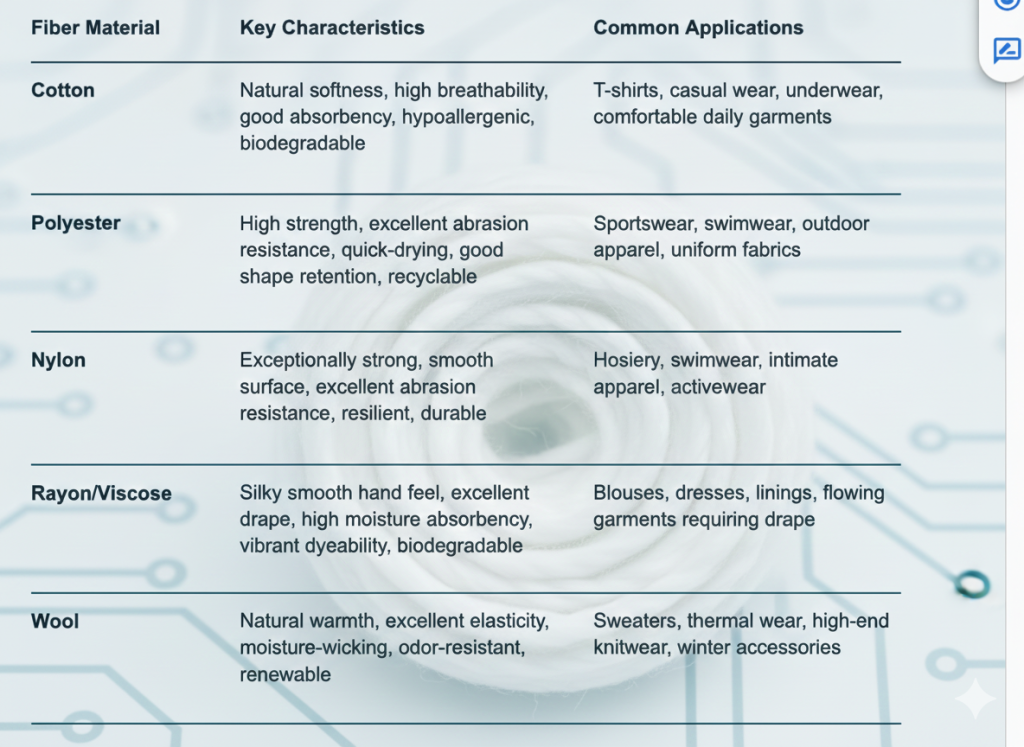
Overview of Common Covering Yarn Materials
| Fiber Material | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
| Cotton | Natural softness, high breathability, good absorbency, hypoallergenic, biodegradable | T-shirts, casual wear, underwear, comfortable daily garments |
| Polyester | High strength, excellent abrasion resistance, quick-drying, good shape retention, recyclable | Sportswear, swimwear, outdoor apparel, uniform fabrics |
| Nylon | Exceptionally strong, smooth surface, excellent abrasion resistance, resilient, durable | Hosiery, swimwear, intimate apparel, activewear |
| Rayon/Viscose | Silky smooth hand feel, excellent drape, high moisture absorbency, vibrant dyeability, biodegradable | Blouses, dresses, linings, flowing garments requiring drape |
| Wool | Natural warmth, excellent elasticity, moisture-wicking, odor-resistant, renewable | Sweaters, thermal wear, high-end knitwear, winter accessories |
Covering Materials
Covering yarns are selected based on their inherent fiber properties, which must complement the elastic core to achieve the desired performance in the final fabric. These materials fall into two primary categories: natural and synthetic fibers, each offering distinct advantages.
Natural Fibers, including cotton and wool are prized for their comfort and breathability. Cotton provides a soft, natural hand feel against the skin and is highly absorbent, while wool offers exceptional inherent elasticity and thermal regulation. From an environmental perspective, natural fibers are generally biodegradable and come from renewable sources, though conventional cotton farming can be water-intensive and may involve pesticide use.
Synthetic Fibers, such as polyester and nylon provide high strength, resilience, and excellent resistance to abrasion. Rayon, a semi-synthetic derived from wood pulp, offers a luxurious drape and sheen. Environmentally, synthetic fibers face challenges with microplastic shedding and are derived from non-renewable petroleum resources. However, the development of recycled alternatives (rPET, recycled nylon) and closed-loop production processes for rayon are helping to mitigate these impacts.
These environmental considerations are increasingly influencing business decisions, with many manufacturers now prioritizing:
- Sustainable sourcing of natural fibers (organic cotton, responsible wool)
- Recycled content in synthetic fibers to support circular economy
- Certifications such as GRS (Global Recycled Standard) and Oeko-Tex
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate covering material requires balancing performance requirements with environmental considerations and comfort goals. The optimal choice depends entirely on the end-use application, whether prioritizing cotton’s natural comfort, synthetic fibers’ durability, or specialized properties like wool’s insulation or rayon’s drape. Understanding these material characteristics enables manufacturers to make informed decisions that align with both performance targets and sustainability objectives.
Need help selecting the ideal covering yarn for your application? Contact our technical experts today for personalized recommendations and samples tailored to your specific requirements.
TANI THREAD CO., LTD
- Address: Thanh Hoa Hamlet, Thanh Dien Commune, Chau Thanh District, Tay Ninh Province, Vietnam
- Hotline: 0984.841.239
- Email: sale@tanithread.com
- Website: tanithread.com



